Germany Roulette War Strategy and its Crushing Defeat During World War II History analysis by Sherif S. Monem
Germany Roulette War Strategy Defeat World War II History analysis Sherif S. Monem
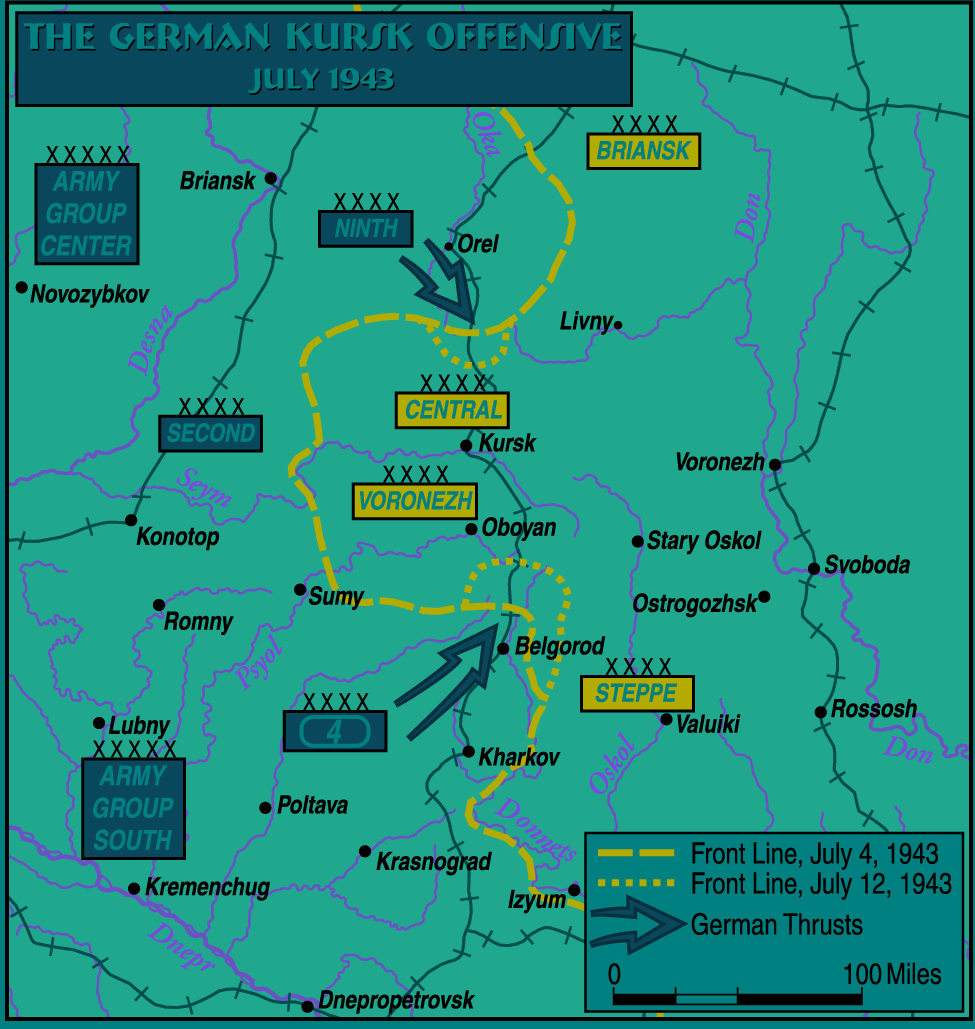
Manstein regarded the Battle of Kursk as something of a German victory, as he believed that he had destroyed much of the Red Army's offensive capacity for the rest of 1943. This assessment turned out to be incorrect, as the Red Army was able to recover much more quickly than Manstein expected. Manstein moved his panzer reserves to the Mius River and the lower Dnieper, not realising the Soviet activities there were a diversion. A Soviet offensive that began on 3 August put Army Group South under heavy pressure. After two days of heavy fighting, the Soviet troops broke through the German lines and retook Belgorod, punching a 56 km (35 mi) wide hole between the Fourth Panzer Army and the Army Detachment Kempf, tasked with holding Kharkov. In response to Manstein's demands for reinforcements, Hitler sent the Großdeutschland, 7th Panzer, SS 2nd Das Reich, and SS 3rd Totenkopf Divisions.



Since at least 1943, it was becoming increasingly clear that Germany would fold under the pressure of the Allied forces. In February of that year, the German 6th Army, lured deep into the Soviet Union, was annihilated at the Battle of Stalingrad, and German hopes for a sustained offensive on both fronts evaporated. Then, in June 1944, the Western Allied armies landed at Normandy, France, and began systematically to push the Germans back toward Berlin. By July 1944, several German military commanders acknowledged their imminent defeat and plotted to remove Hitler from power so as to negotiate a more favorable peace.
Their attempts to assassinate Hitler failed, however, and in his reprisals, Hitler executed over 4,000 fellow countrymen.
Germany war strategy decisions that caused its collapse and ultimate defeat was caused by Russian Roulette mentality and also to the impulsive behavior.
Russian campaign was a roulette gambling mentality.Not sure of wining they.indulged in such campaign at great risk. When it appeared they are losing the gamble they did not pull the chair of the Roulette sampling table.
The Kursk offensive was failure and very costly. To make things worse Hitler over ruled general Manstein suggestion to begin the military campaign in earnest and this was to the advantage to the Russians to bolster their defenses through laying mine fields and what else. It was better for these German troupes to retreat to defend their home land from invasion.
Manstein regarded the Battle of Kursk as something of a German victory, as he believed that he had destroyed much of the Red Army's offensive capacity for the rest of 1943. This assessment turned out to be incorrect, as the Red Army was able to recover much more quickly than Manstein expected. Manstein moved his panzer reserves to the Mius River and the lower Dnieper, not realising the Soviet activities there were a diversion. A Soviet offensive that began on 3 August put Army Group South under heavy pressure. After two days of heavy fighting, the Soviet troops broke through the German lines and retook Belgorod, punching a 56 km (35 mi) wide hole between the Fourth Panzer Army and the Army Detachment Kempf, tasked with holding Kharkov. In response to Manstein's demands for reinforcements, Hitler sent the Großdeutschland, 7th Panzer, SS 2nd Das Reich, and SS 3rd Totenkopf Divisions.




| Commanders and leaders | |
|---|---|
Casualties
Battle of Kursk:
After this battle Russia was on winning streak.
http://www.history.com/topics/world-war-ii/battle-of-kursk
Since at least 1943, it was becoming increasingly clear that Germany would fold under the pressure of the Allied forces. In February of that year, the German 6th Army, lured deep into the Soviet Union, was annihilated at the Battle of Stalingrad, and German hopes for a sustained offensive on both fronts evaporated. Then, in June 1944, the Western Allied armies landed at Normandy, France, and began systematically to push the Germans back toward Berlin. By July 1944, several German military commanders acknowledged their imminent defeat and plotted to remove Hitler from power so as to negotiate a more favorable peace.
Their attempts to assassinate Hitler failed, however, and in his reprisals, Hitler executed over 4,000 fellow countrymen.

Comments
Post a Comment